Gilson Inc의 'Automation of RT-qPCR for Promega’s GoTaq® Probe 1-Step RT-qPCR Kit'를 이용한 응용자료는 한국분석기기(주)에서 제공하였으며 주요 내용은 다음과 같다.
INTRODUCTION
Reverse transcription quantitative PCR(RT-qPCR)
is a highly sensitive assay for detection of RNA and is the predominant method implemented into the RT-qPCR workflow for detection of viral RNA. Manually extracting viral RNA and plate setup of RT-qPCR is time consuming and laborious.
This application note describes the automation of RNA extraction on the Promega Maxwell® 16 system and the GoTaq® Probe 1-Step RT-qPCR system on the Gilson PIPETMAX® 268.
RNA extraction and RT-qPCR were both shown to be superior to the manual methods in terms of time-savings and reproducibility.
The amount of amplifiable nucleic acid is dependent on multiple factors including the degree of degradation, co-purification of contaminants that may experiments(common in FFPE preserved samples).
Amplification conditions will also influence success(e.g. amplicon size, reagents and primer design). Promega GoTaq® amplification reagents, such as the GoTaq® Probe 1-Step RT-qPCR system, were specifically designed to be highly robust and resistant to enzyme inhibitors, improving the quality of the results.
In this study, functional RNA was quantitated by RT-qPCR using the GoTaq® Probe 1-Step RT-qPCR System after two different extraction methods: Promega’s Maxwell® 16 LEV(low elution volume) RNA Kit and a competitor spin column-based RNA extraction kit. To enhance the pipetting accuracy and consistency an automated pipetting assistant, Gilson PIPETMAX 268, was used to reduce pipetting errors inherent in manual methods(Figure 1).
- Automated with Promega - Automated with - Automated with PIPETMAX® - Export run file from qPCR
MAXWELL® 16 PIPETMAX® qPCR qPCR Assistant Assistant; import run file
- vs. spin column extraction - vs. manual - Amplified with GoTaq® Probe into thermocycler
with competitor kit 1-Step RT-qPCR system
MATERIALS AND METHODS
RNA Extraction
Automated isolation of RNA was carried out according to manufacturer’s instructions using the Maxwell® 16. RNA purifications were performed in replicates of 6 following the manufacturer recommendations(Promega Technical manual - TM415). Spin column RNA isolation was carried out according to manufacturer’s instructions using a competitor’s RNA kit.
Quantitative RT-PCR
TaqMan® Primers and Probe were obtained from Life Technologies.
The PIPETMAX qPCR Assistant software(Gilson) creates 3 separate protocols for the reaction preparation(master mix preparation, sample/standard dilution, and qPCR plate protocol); all three steps were completed on PIPETMAX.
For greates consistency, master inhibit enzymatic assays, and DNA integrity in cross linking mixes prepared by PIPETMAX were mixed manually after assembly. The standard curve was amplified in triplicate, using the control total RNA diluted in 4-fold steps from 500ng/μl to 0.12ng/μl. Samples were amplified in replicates of six(n=6) at a 1:10 dilution(dilutions were completed on the PIPETMAX) to bring the concentrations within the standard curve range. For comparison to manual amplifications, the standard and samples(neat and 1:10 dilution) were amplified in duplicate. The RNA eluates were amplified on a Bio-Rad CFX96 Real-Time System using the GoTaq® Probe 1-Step RT-qPCR System according to manufacturer’s recommendations Technical(Promega manual - TM379). All reactions were prepared with fixed volume(2μl) sample additions in a final volume of 20μL.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
RNA was isolated using two different methods:
the semi-automated Maxwell® 16 system and a competitor manual spin column-based method. To determine the amount of amplifiable RNA, the eluates were reverse transcribed and amplified using the GoTaq® probe 1-step RT-qPCR system. The PIPETMAX was used to prepare sample dilutions control RNA standard serial dilutions, and amplification reactions.
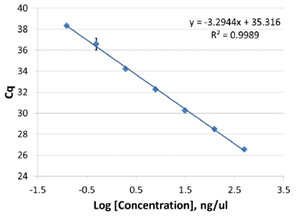
The control standard curve yielded a linear fit analysis with an R2 value of 0.9989, with minimal variation between replicates (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Control standard curve used to calculate the amount of amplifiable RNA in sample purifications. All amplification reactions
were prepared on the PIPETMAX. Cq values are shown as AVG ± 1SD for n=3.
All amplification reactions resulted in Cq values that fit within the standard curve, allowing for the determination of all eluate concentrations.
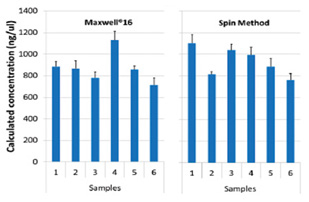
The calculated RNA concentrations were similar between the two isolation methods(Figure 3).
Figure 3. Calculated concentrations of amplifiable RNA in sample isolations. RNA was purified from replicate samples using either the Maxwell®16 or a competitor spin method. All amplification reactions were prepared in sextuplet on the PIPETMAX.
Concentrations are shown as AVG ± 1SD(n=6).
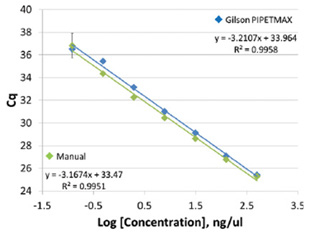
The Maxwell® 16 System is just as efficient at isolating amplifiable RNA as the competitor spin method while also enabling a walkaway sample. To evaluate the PIPETMAX pipetting accuracy and variability versus manual pipetting, we tested the linear fit of a serial diluted standard and variability of sample quantitation when amplified using RT-qPCR. A standard curve was made by serially diluting the control RNA both manually and on the PIPETMAX. Both the manual and PIPETMAX standard curves were very good with R2 values of 0.996 and 0.995 respectively(Figure 4).
Figure 4. Control standard curves prepared manually as well as on the PIPETMAX. Cq values are shown as AVG ± 1SD(n=2).
The manual standard curve did show more variation on the last dilution point and had a slightly lower slope(-3.17 to -3.21, respectively).
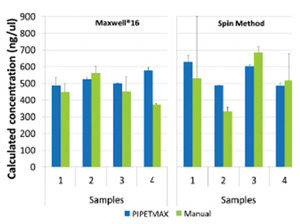
Additional RNA samples were quantitated using qPCR reactions prepared on the PIPETMAX qPCR Assistant or manually. The calculated RNA concentrations between the PIPETMAX and manual amplifications were comparable; however, the manually pipetted samples were consistently more variable than the ones prepared on the PIPETMAX(Figure 5).
Figure 5. Calculated concentrations of amplifiable RNA in sample isolations. RNA was purified using the Maxwell® 16 or a competitor spin method. Amplification reactions were prepared using PIPETMAX or manually. Data are shown as AVG ± 1SD(n=2).
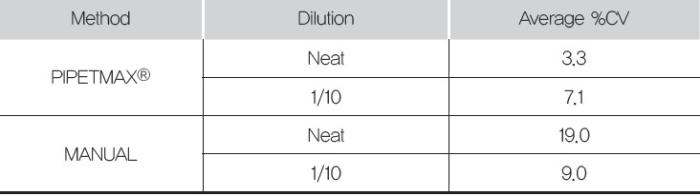
An analysis of the %CV values from these data show that the PIPETMAX had lower values as compared to the manual preparation(Table 1).
This indicates that the PIPETMAX can pipet reagents with less error than a scientist pipetting manually.
Table 1. Average %CV from the sample amplifications (duplicate amplifications of quadruplicate purifications). Purifications were carried out using the Maxwell® 16.
SUMMARY
• The Promega Maxwell® 16 instrument provides consistent RNA purifications with minimal preprocessing.
• The instrument enables walkaway purification, allowing greater productivity in other areas of the lab.
• The RNA purifications from the Maxwell® 16 had similar yields and quality as the more time intensive and laborious competitor spin method.
• Integration of the PIPETMAX with the GoTaq® Probe 1-Step RT-qPCR System provided a convenient and consistent method of automating the preparation and execution of the amplification-based quantitation assay.
• Further testing showed the PIPETMAX qPCR Assistant is a good substitute for manual preparation of amplification reactions and can help reduce variability introduced through manual pipetting.
Gilson Inc의 'Automation of RT-qPCR for Promega’s GoTaq® Probe 1-Step RT-qPCR Kit'에 대한 궁금한 내용은 본 원고자료를 제공한 한국분석기기(주)를 통하여 확인할 수 있다.
Reference(참고문헌): Commission Regulation(EC) No 1881/2006 Corn samples were used for this application note. Corn Total RNA(Zyagen, Cat. #PLR-1002) was used as a positive control. TaqMan® Corn Primers and Probe [Cat. #Zm04073989_m1 (zmm19)] were obtained from Life Technologies.
Gilson Application note 1031.
Model Name(모델명): PIPETMAX
The Person in Charge(담당자): An Hyesook
Maker(제조사): Gilson Inc.
Country of Origin(원산지): U.S.A
Data Services(자료제공): Gilson Inc.
<이 기사는 사이언스21 매거진 2020년 6월호에 게재 되었습니다.>